This writing is provided in English first, followed by Korean.
이 글은 영어 -> 한국어 순으로 작성되어 있습니다.An Autoencoder
- an unsupervised neural network
- that learns to compress (encode) data into a low-dimensional representation
- and then reconstruct (decode) it back to its original form. - Its primary goal is to learn the most essential features of the data, captured in a compressed "latent space."
1. Introduction
1.1. Definition
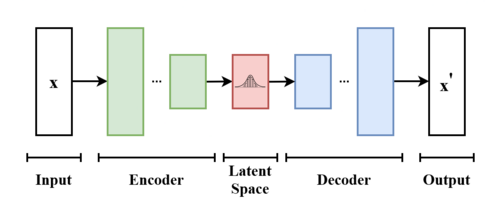
An Autoencoder is an unsupervised neural network that learns to compress (encode) data into a low-dimensional representation and then reconstruct (decode) it back to its original form. Its primary goal is to learn the most essential features of the data, captured in a compressed "latent space," by training the network to reconstruct its own input.
1.2. Types
Autoencoders come in several variations, each with unique constraints and use cases:
- Undercomplete Autoencoders: The simplest form, where the bottleneck layer is smaller than the input, forcing the network to learn the most salient features for dimensionality reduction.
- Regularized Autoencoders: A broader class that uses regularization techniques to prevent overfitting and learn more robust features. This includes the types below.
- Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs): Constrains the number of neurons that can be active at one time. This allows the network to have a large capacity while forcing it to learn specific features with different nodes.
- Denoising Autoencoders: Trained to reconstruct a clean, original input from a partially corrupted version. This forces the model to learn robust features and ignore noise.
- Contractive Autoencoders: Designed to be insensitive to small variations in the input data, encouraging the model to learn features that capture the underlying structure rather than minor details.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): Learns the parameters of a probability distribution representing the data. This makes it a generative model, capable of creating new data samples by sampling from this distribution.
1.3. Structures
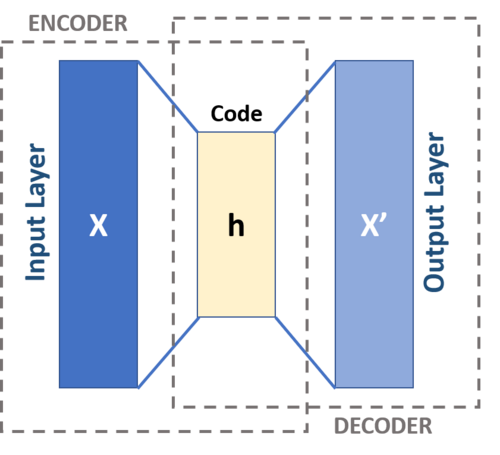
The structure of an autoencoder is composed of two main parts: the Encoder and the Decoder.
Encoder
The Encoder's job is to compress the input data. It takes the high-dimensional input (like an image) and passes it through a series of layers that progressively reduce the dimensions. The final output is a compact, low-dimensional representation, often called the bottleneck or latent representation.
Decoder
The Decoder's job is to reconstruct the original data from the compressed representation. It takes the low-dimensional output from the encoder and passes it through a series of layers that progressively increase the dimensions, aiming to recreate the input as accurately as possible.
Comparison: Encoder vs. Decoder
| Feature | Encoder | Decoder |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Compresses data into a latent representation. | Reconstructs data from the latent representation. |
| Architecture | The number of neurons decreases with each layer. | The number of neurons increases with each layer. |
| Input & Output | Input: Original Data\<br>Output: Latent Representation | Input: Latent Representation\<br>Output: Reconstructed Data |
2. Application
Autoencoders are well-suited for tasks that benefit from learning the underlying structure of data in an unsupervised manner.
2.1. Dimensionality Reduction
By learning a compressed representation, autoencoders can be used to reduce the number of features in a dataset. This is useful for data visualization and can improve the performance of other models.
2.2. Image and Audio Denoising
An autoencoder can be trained on clean data and then used to clean up noisy inputs. It reconstructs a clean version from a corrupted input, effectively filtering out the noise.
2.3. Generative Tasks
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) can generate new data. By sampling points from the learned latent space, the decoder can create new, plausible data samples that resemble the original training data.
2.4. Anomaly Detection and Facial Recognition
Autoencoders are excellent for detecting outliers. Trained only on "normal" data, they produce a high reconstruction error for anomalous inputs, signaling a deviation. This can be used for fraud detection or confirming a genuine match.
1. 개요
1.1. 정의
오토인코더(Autoencoder)
- 데이터를 저차원 표현으로 압축(인코딩)하고
- 다시 원본 형태로 복원(디코딩)하도록 학습하는 비지도 학습 신경망.
- 스스로 자기 자신의 입력을 재구성하고 압축된 잠재 공간에 데이터의 가장 본질적인(essential) 특징을 학습하는 것을 주요 목표로 함.
1.2. 종류
데이터 조건과 환경 등에 맞추어 여러 버전의 오토인코더가 있음.
- 과소완전 오토인코더 (Undercomplete Autoencoders): 가장 단순한 형태. 병목 계층이 입력보다 작아 네트워크가 차원 축소를 위해 가장 두드러진 특징을 학습하도록 강제함.
- 정규화 오토인코더 (Regularized Autoencoders): 과적합을 방지하고 더 강한 특징을 학습하기 위해 정규화 기법을 사용. 더 넓은 범위이며 아래 오토인코더들 포함
- 희소 오토인코더 (Sparse Autoencoders): 한 번에 활성화될 수 있는 뉴런의 수를 제한. => 네트워크가 큰 용량을 가지면서도 다른 노드로 특정 특징을 학습하도록 강제함.
- 잡음 제거 오토인코더 (Denoising Autoencoders): 부분적으로 손상된 입력으로부터 깨끗한 원본 입력을 재구성하도록 학습됨. 이는 모델이 강건한(robust) 특징을 배우고 노이즈를 무시하도록 강제함.
- 축소 오토인코더 (Contractive Autoencoders): 입력 데이터의 작은 변화에 둔감하도록 설계 => 모델이 사소한 디테일보다 근본적인 구조를 포착하는 특징을 학습하도록 함.
- 변이형 오토인코더 (Variational Autoencoders): 데이터를 나타내는 확률 분포의 매개변수를 학습 => 잠재 공간 분포에서 샘플링하여 (새로운 데이터를 생성할 수 있는) 생성 모델이 됨.
1.3. 구조
오토인코더의 구조는 인코더와 디코더, 두 가지 주요 부분으로 구성됨.
인코더 (Encoder)
입력 데이터를 압축하는 역할. 고차원 입력을 받아 점진적으로 차원을 축소하는 신경망 층을 통과시킴. 최종 출력은 데이터의 압축된 저차원 표현이며, 병목(bottleneck) 또는 잠재 표현(latent representation) 이라 말함.
디코더 (Decoder)
압축된 표현으로부터 원본 데이터를 복원하는 역할. 인코더의 저차원 출력을 받아 점진적으로 차원을 확대하는 신경망 층을 통과시켜, 가능한 한 원본 입력과 가깝게 재구성하는 것을 목표로 함.
비교: 인코더 vs. 디코더
| 특징 | 인코더 | 디코더 |
|---|---|---|
| 목적 | 데이터를 잠재 표현으로 압축 | 잠재 표현으로부터 데이터 복원 |
| 구조 | 신경망 층이 진행될수록 뉴런 수 감소 | 신경망 층이 진행될수록 뉴런 수 증가 |
| 입력 & 출력 | 입력: 원본 데이터 출력: 잠재 표현 | 입력: 잠재 표현 출력: 복원된 데이터 |
2. 적용 분야
오토인코더는 비지도 방식으로 데이터의 근본적인 구조를 학습하는 것이 유용한 작업에 매우 적합함.
2.1. 차원 축소
데이터의 압축된 표현을 학습하여 데이터셋의 특징 수를 줄이는 데 사용. 데이터 시각화에 유용하며 다른 모델의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있음.
2.2. 이미지 및 오디오 노이즈 제거
깨끗한 데이터로 학습시킨 후 노이즈가 낀 입력을 정리하는 데 사용. 손상된 입력으로부터 깨끗한 버전을 재구성하여 효과적으로 노이즈를 필터링함.
2.3. 생성
변이형 오토인코더(VAE)는 새로운 데이터를 생성할 수 있음. 학습된 잠재 공간에서 포인트를 샘플링하여, 디코더가 원본 학습 데이터와 유사한 새로운 데이터를 만들어 냄.
2.4. 이상 탐지 및 얼굴 인식
이상치를 탐지하는 데 탁월함. "정상" 데이터로만 학습되어 비정상적 입력에 대해 높은 재구성 오류를 생성하며, 이는 편차를 나타내는 신호가 됨. 사기 탐지나 진위 여부 확인에 사용될 수 있음.
Reference
Image
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/autoencoder
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoencoder
https://www.v7labs.com/blog/autoencoders-guide
